
February 8, 2023
The Hidden Risks & Importance of Cybersecurity in M&A
By Apexa iQ
As a merger & acquisition (M&A) deal progresses through its lifecycle, cybersecurity and data privacy risks steadily increase.
What is the role of cybersecurity in M&A?
Cybersecurity due diligence is important in M&A because it provides insight into potential cyber risks and how they could affect the success of the transaction. It helps protect confidential information and company data from malicious actors who might try to use the information for personal gain.
Without proper cybersecurity due diligence in M&A, risks can be significant. In recent years, some companies are setting aside a percentage of the total transaction for the potential fallout of an impending attack. According to a recent article from Gartner, by 2025, 60% of organizations will use cybersecurity risk as a primary determinant in conducting M&A transactions and business engagements.
The Benefits of Cybersecurity in M&A
Higher Success Rates: Improve the number of M&A deals that are successful and avoid fines or the cost of losing the trust of customers, partners, and investors.
Negotiations Leverage: Strengthen your negotiations for more favorable valuations by developing a proactive plan to leverage cybersecurity as a tool.
Know Where You Stand: Get a comprehensive view of the intellectual property and technological assets of the target organization.
Reduce Costs: Reduce the time and other resources needed to meet investment goals.
Productivity: Stave off costly disruptions in workflow or employee productivity by better protecting data, networks, and systems.
Enhance Security: Uncover dormant threats early on to prevent putting a deal in jeopardy or losing revenue after the deal closes.
Keep Customers Safe: Keep customer data private and compliant with data compliance regulations.
The Cybersecurity Lifecycle for M&A
The M&A cybersecurity lifecycle consists of four steps.
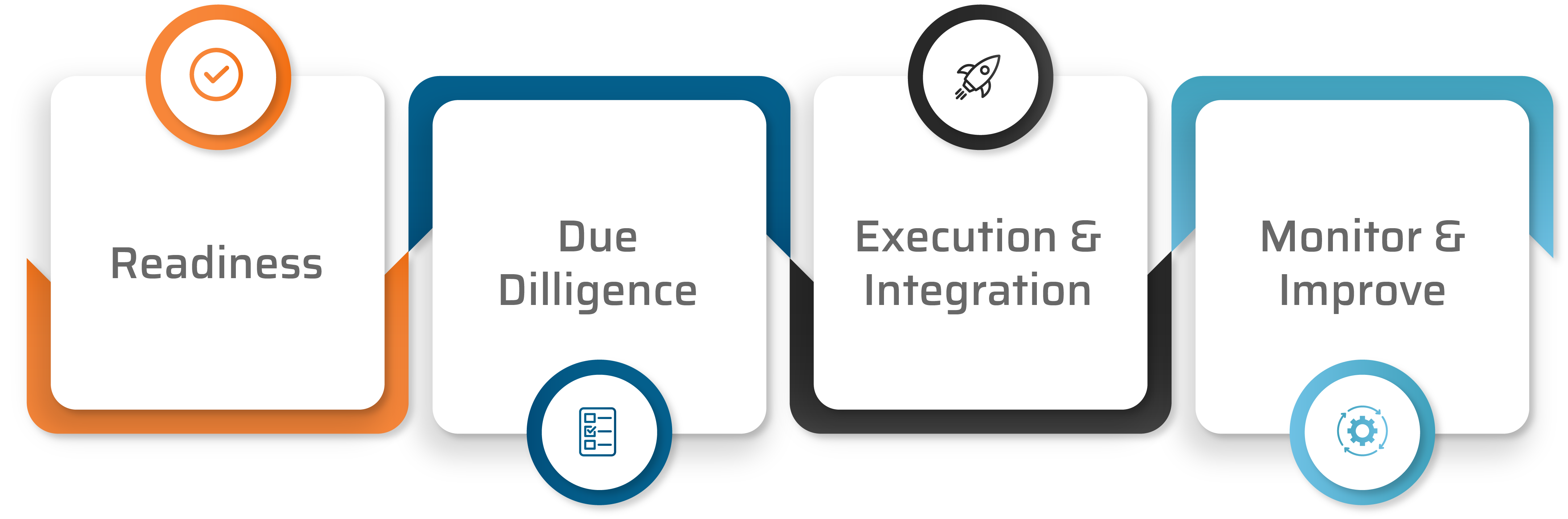
- Readiness: Begin planning from the start of the M&A. This first phase involves analyzing the posture, including defining the composition and qualifications of the target’s infosec team and getting clarity on the target’s security hygiene. Assessing the risk of the target’s security hygiene should include identifying all third-party dependencies.
- Due Diligence: Conduct cybersecurity risk and data compliance assessments along with identifying the potential ongoing cost of cybersecurity to factor into the deal price.
- Execution & Integration: Remediate the risks to get the target organization to a healthy security posture with systems and data. Then integrate the target company’s security environment into the acquiring company’s existing security framework.
- Monitor & Improve: Continue to monitor for vulnerabilities and compliance risks. Have regular meetings to discuss the current state and remediation efforts.
Risks of Not Prioritizing Cybersecurity in M&A
It’s critical to uncover how robust the target’s data security and information technology practices are from the start. Know how serious the company is about data privacy compliance at the beginning of the M&A lifecycle. In an effort to protect against threats to national security and the data of citizens, M&A regulators are scrutinizing deals and issuing fines for non-compliance. New regulations such as General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) and California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) both require that companies take steps to ensure that any personally identifiable data that is being transferred between entities as part of a deal is done so securely and in compliance with the applicable regulations.
Acquiring companies with bad cybersecurity posture will make it easier for dormant hackers to strike. If a breach occurs due to inadequate cybersecurity measures, organizations risk reputational damage and the erosion of customer, partner, and employee trust. Buyers must be thorough to uncover the amount of risk in the seller’s assets and the seller wants to manage transactional risk. Both the buyers and the sellers want to manage post-closing risks.
How to Create a Proactive Cybersecurity Plan Before an M&A
Develop a proactive plan to conduct due diligence through risk profiling. During the process, the buyer and seller collaborate to assess the target company’s current cybersecurity posture, identify gaps, and agree on the level of acceptable risk. This process can help reduce the financial risk of a possible data breach. Risk associated with a data breach includes costs to recover from and respond to an attack, research and legal fees, lost market, reputation damage, lower staff morale, and potential financial penalties. Having a plan can also reduce the M&A lifecycle because you have a plan to uncover risk and can start from the beginning.
Having a cybersecurity due diligence playbook is recommended. Here are key steps for your organization’s playbook:
- At the beginning of the M&A, identify the scope and objectives of cybersecurity due diligence for the target company.
- Assess the cybersecurity processes and procedures that are currently in place. Then, identify what processes and procedures are not in place for implementation.
- Evaluate the technology infrastructure and identify the target’s known weaknesses by using an asset assurance platform, such as ApexaiQ®.
- Analyze the target’s security posture of their suppliers, vendors, and third-party service providers.
- Perform data management and protection audits.
- Establish policies and procedures for cybersecurity threats, breaches, and incidents.
Not only should you document this playbook for repeatable and successful due diligence, but you should also continually challenge the playbook and its assumptions to evolve with the cybersecurity threat landscape.


